Structure and Function of a URL 🕸️👨💻🖥️
Part 2/2: A Guide to Understanding the Backbone of the Internet
A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is a web address used to access resources on the internet. By understanding URL components, navigating the web becomes clearer and more intuitive. Each part works together to ensure you find and access the information or resource you're seeking efficiently.
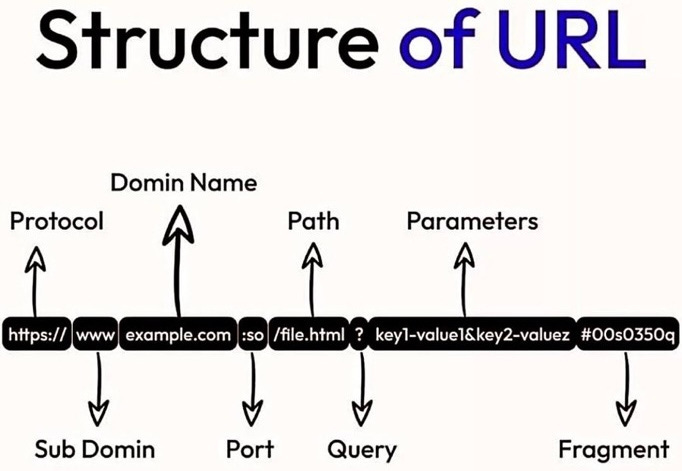
URL breaks down into its specific parts using the image above:
Protocol (https://): Defines the method used to access the resource (e.g., HTTP, HTTPS).
Subdomain (www): A subdivision of the main domain.
Domain Name (example.com): The main address of the website.
Port (:80): A communication endpoint. Default ports like 80 for HTTP are often omitted.
Path (/file.html): The specific location of a file/resource on the server.
Query (?key1=value1&key2=value2): Data sent to the server, usually for dynamic content.
Parameters: The actual values in the query.
Fragment (#00s0350q): A section within the resource, often a specific part of the web page.
Detailed Breakdown: